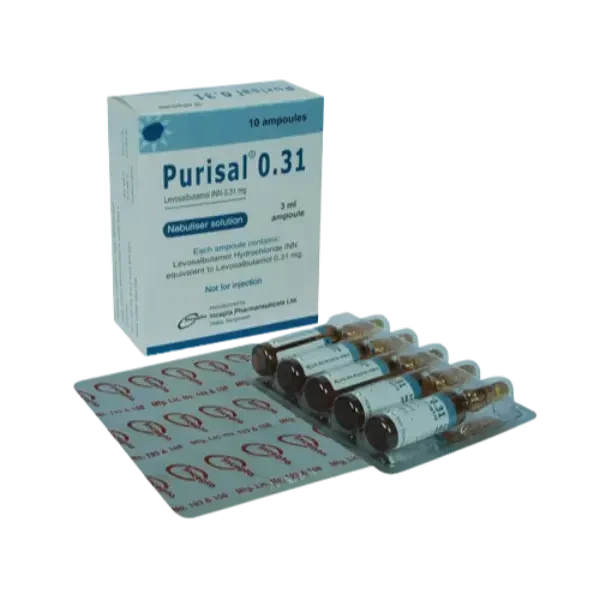
ndications of Minicon
Minicon tablets are indicated for use by females of reproductive potential to prevent pregnancy. This tablet are not for use as emergency contraception.
Theropeutic Class
Emergency Contraceptive Pill, Oral Contraceptive preparations
Pharmacology
Minicon (and more specifically the active stereoisomer levoMinicon ) binds to the progesterone and estrogen receptors within the female reproductive tract, the mammary gland, the hypothalamus, and the pituitary. Once bound to the receptor, progestins like levoMinicon will slow the frequency of release of gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH) from the hypothalamus and blunt the pre-ovulatory LH (luteinizing hormone) surge. Loss of the LH surge inhibits ovulation and thereby prevents pregnancy.
Dosage & Administration of Minicon
0.075 mg at same time each day
Dosage of Minicon
To achieve maximum contraceptive effectiveness, Minicon Tablets must be taken exactly as directed. The woman should take one tablet every day, at the same time. The administration is continuous, with no interruption between pill packs.
Contraindications
Minicon tablet is contraindicated for use by women who are known to have the following conditions: Known or suspected pregnancy Known or suspected carcinoma of the breast, or other progestin-sensitive cancer, now or in the past Undiagnosed abnormal uterine bleeding Hypersensitivity to any component of this product Benign or malignant liver tumors
Side Effects of Minicon
An increased risk of the following adverse reactions has been reported with the use of progestin-only oral contraceptives: Delayed follicular atresia/ovarian cysts, Menstrual irregularity, changes in menstrual flow; breakthrough bleeding/spotting; amenorrhea, prolonged bleeding. The following adverse reactions were reported in ≥5% of subjects in the Minicon Tablet clinical studies: Headache Dizziness Nausea Increased appetite Abdominal pain, cramps and bloating Fatigue Vaginal discharge Dysmenorrhea Nervousness Backache Breast discomfort Acne
Pregnancy & Lactation
Pregnancy Category: XLactation: unsafe
Precautions & Warnings
Migraine/Headache: The onset or exacerbation of migraine, or development of headache with a new pattern that is recurrent, persistent, or severe requires evaluation of the cause because women with migraine may be at increased risk of stroke.Drug Interactions: The effectiveness of progestin-only pills is reduced by hepatic enzyme-inducing drugs such as phenytoin, carbamazepine, barbiturates, rifampin, efavirenz, bosentan and herbal preparations containing St. John’s Wort (hypericum perforatum ). This could result in unintended pregnancy or breakthrough bleeding. During concomitant use of Minicon and substances that may affect its efficacy, it is recommended that a nonhormonal back-up method of contraception (such as condom) be used in addition to the regular intake of Minicon Tablets. Use of a nonhormonal back-up method is recommeded for 28 days after discontinuation of substances that have led to induction of hepatic microsomal enzymes. For women receiving long-term therapy with hepatic enzyme inducers, another method of contraception should be considered. Effectiveness of progestin-containing hormonal contraceptives and emergency contraceptive ulipristal acetate may be decreased if progestin-containing hormonal contraceptives are used within five days after ulipristal acetate dosing. If a woman wishes to use Minicon Tablets after using ulipristal acetate, she should do so no sooner than 5 days after the intake of ulipristal acetate and she should use a reliable barrier method for subsequent acts of intercourse until her next menstrual period. Gastrointestinal: Diarrhea and/or vomiting within 4 hours after taking a pill may reduce hormone absorption. Women should use of a nonhormonal back-up method of birth control (such as a condom or spermicide) during the next 48 hours.Interactions with Laboratory Tests: The following endocrine tests may be affected by Minicon Tablets use: Sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG) concentrations may be decreased. Total thyroxine concentrations may be decreased, due to a decrease in thyroid binding globulin (TBG). However, free thyroxine level should remain unchanged.
Overdose Effects of Minicon
Symptoms of oral contraceptive overdosage may include nausea, vomiting, breast tenderness, dizziness, somnolence ( drowsiness/fatigue), and withdrawal bleeding in females. There is no specific antidote and further treatment of overdose, if necessary, is directed to the symptoms.
Storage Conditions
Store at controlled room temperature between 20° to 25°C.
Drug Classes
Oral Contraceptive preparations
Mode Of Action
Progestin-only oral contraceptives such as Minicon tablets prevent conception by suppres sing ovulation in approximately half of the cycles in users, thickening the cervical mucus to inhibit sperm penetration, lowering the midcycle LH and FSH peaks, slowing the movement of the ovum through the fallopian tubes, and altering the endometrium. Serum progestin levels peak about two hours after oral administration, followed by rapid distribution and elimination. By 24 hours after drug ingestion, serum levels are near baseline, making efficacy dependent upon rigid adherence to the dosing schedule. There are large variations in serum levels among individual users. Progestin-only administration results in lower steady-state progestin levels and a shorter elimination half-life than concomitant administration with estrogens.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy: Minicon Tablets are contraindicated for use in pregnant women because there is no need for pregnancy prevention in a woman who is already pregnant. Published studies report no harmful effects on fetal development associated with long-term use of contraceptive doses of oral progestins in pregnant women. Discontinue Minicon Tablets if pregnancy is confirmed.Nursing Mothers: Small amounts of progestin pass into the breast milk, resulting in steroid levels in infant plasma. No adverse effects have been reported on breastfeeding performance or infant health. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for Minicon Tablets and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from Minicon Tablets or from the underlying maternal condition.
Pediatric Uses
Pediatric Use: The safety and efficacy of Minicon tablets have been established in women of reproductive age, including adolescents as young as 15 years of age, and almost 30% of subjects in the clinical trials who were under 20 years of age. Use of this product before menarche is not indicated.Geriatric Use: Minicon tablet Tablets have not been studied in postmenopausal women and is not indicated in this population

 Fast Delivery meahbazar area
Fast Delivery meahbazar area
 Safe Payment
Safe Payment
 7 Days Return Policy
7 Days Return Policy
 100% Authentic Products
100% Authentic Products